Pathologists and medical technologists play crucial roles in the healthcare system, working behind the scenes to provide essential diagnostic and laboratory services. From analyzing tissue samples to performing complex laboratory tests, these professionals contribute to accurate diagnoses, treatment decisions, and patient care. In this article, we explore the roles of pathologists and medical technologists in healthcare, highlighting their invaluable contributions to the field of medicine.
Pathologists:
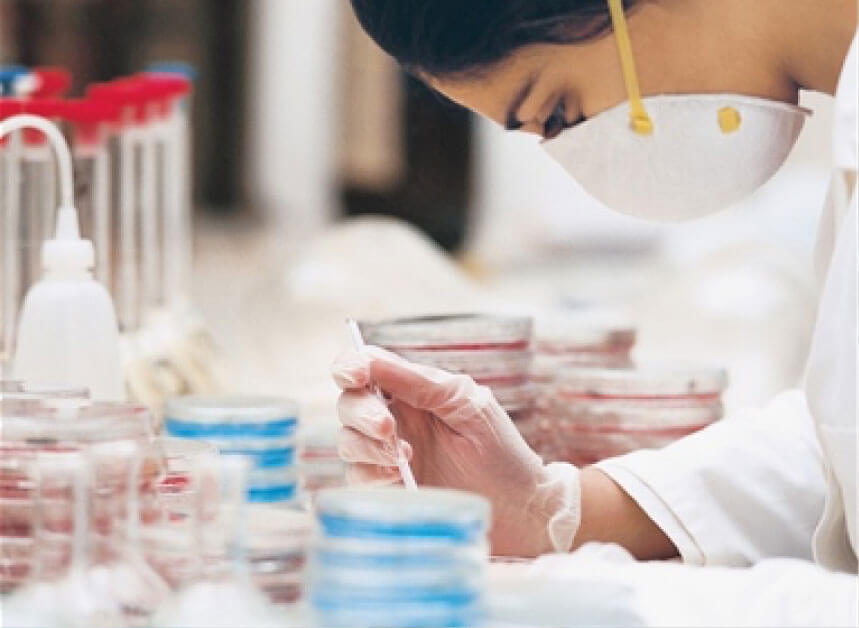
Pathologists are medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and characterization of disease through the examination of tissue samples, blood samples, and other bodily fluids. Their expertise lies in interpreting laboratory test results, identifying abnormalities, and providing diagnostic insights to guide patient care. Pathologists play a critical role in diagnosing conditions such as cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders, helping to inform treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Tissue Examination: Pathologists examine tissue samples obtained from biopsies, surgeries, or autopsies to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, inflammation, or infection. Using a microscope and other laboratory techniques, they analyze the structure, composition, and cellular characteristics of tissues to make accurate diagnoses.
Laboratory Oversight: Pathologists oversee clinical laboratory operations, ensuring that testing procedures meet quality and safety standards. They develop and validate laboratory tests, interpret test results, and provide consultation to healthcare providers on test selection, interpretation, and clinical significance.
Research and Education: Pathologists are involved in medical research and education, contributing to advancements in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. They conduct research studies, publish scientific articles, and teach medical students, residents, and fellow pathologists about pathology principles and practices.
Medical Technologists:
Medical technologists, also known as clinical laboratory scientists, perform laboratory tests and analyses to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. They work under the supervision of pathologists or laboratory managers, using sophisticated instrumentation and techniques to analyze samples and generate accurate test results. Medical technologists play a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of laboratory testing, contributing to patient care across various medical specialties.
Test Performance: Medical technologists perform a wide range of laboratory tests, including hematology, clinical chemistry, microbiology, immunology, and molecular diagnostics. They follow standardized protocols and procedures to prepare samples, conduct tests, and analyze results, adhering to quality control measures to ensure accurate and reliable outcomes.
Instrumentation and Maintenance: Medical technologists operate and maintain laboratory instrumentation and equipment, including automated analyzers, centrifuges, and microscopes. They troubleshoot instrument malfunctions, perform preventive maintenance, and calibrate instruments to maintain optimal performance and accuracy.
Data Analysis and Reporting: Medical technologists analyze test results, interpret findings, and report data to healthcare providers in a timely and accurate manner. They document test procedures, results, and observations in electronic medical records (EMRs) or laboratory information systems (LIS), ensuring that patient information is recorded and communicated effectively for clinical decision-making.
Pathologists and medical technologists play integral roles in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases in healthcare. From interpreting tissue samples to performing laboratory tests, these professionals contribute to accurate diagnoses, treatment decisions, and patient care. Their expertise, dedication, and commitment to quality ensure that patients receive timely and reliable diagnostic information, leading to improved outcomes and better overall healthcare delivery.























+ There are no comments
Add yours